Feb 06, 2024PRESS RELEASE
Study results accepted by AAAI-24, a top international conference on AI
Rikkyo team develops new image recognition method using Fourier transform
Keyword:RESEARCH
OBJECTIVE.
A new image recognition method using the Fourier transform has been developed by a Rikkyo University team comprising Yuki Tatsunami, a second-year doctoral program student at the Graduate School of Artificial Intelligence and Science who is also an engineer at AnyTech Co., Ltd., and Associate Professor Masato Taki. The results of their study have recently been accepted by the 38th Annual AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-24), one of the top international conferences in the field of artificial intelligence.
Background of research
To avoid this problem, a global filter, which is a fast Fourier transform-based mechanism, has been proposed in recent years as an alternative to the attention mechanism. Similar to the attention mechanism, the global filter can learn long-distance spatial dependencies. The method consists of a fast Fourier transform, element-wise multiplication in frequency domains, and an inverse fast Fourier transform. In contrast to the attention mechanism, this simple system does not require a large amount of memory and only moderately increases in computational complexity as resolution increases. In reality, however, the global filter has not yet achieved state-of-the-art performance.
Results
Now, we have adopted the “dynamic filter,” which dynamically generates a filter to be applied to the data. The dynamic filter calculates weights according to the data and generates a filter according to the weights and a small number of base filters. Using this method can achieve data dependency as in the attention mechanism, while still enjoying the advantages of the global filter.
Next, we have proposed two novel image recognition models: DFFormer, which incorporates the dynamic filter that we have proposed, and CDFFormer, which combines the dynamic filter and a convolutional neural network. There were gaps between the global filter and the attention mechanism, not only in themselves, but also between the macro architectures that employ them. To fill these gaps, we mounted dynamic filters on the architectures that had achieved the highest levels of accuracy and verified the usefulness of the dynamic filters in a fair comparison. These models have achieved accuracy comparable to that of state-of-the-art image recognition models that do not use the attention mechanism. The accuracy has also become closer than before to that of state-of-the-art models that use the attention mechanism, overcoming the previously mentioned problems related to the attention mechanism. In other words, for high-resolution image recognition, our proposed method, similar to the global filter, requires relatively small memory consumption and computation time.
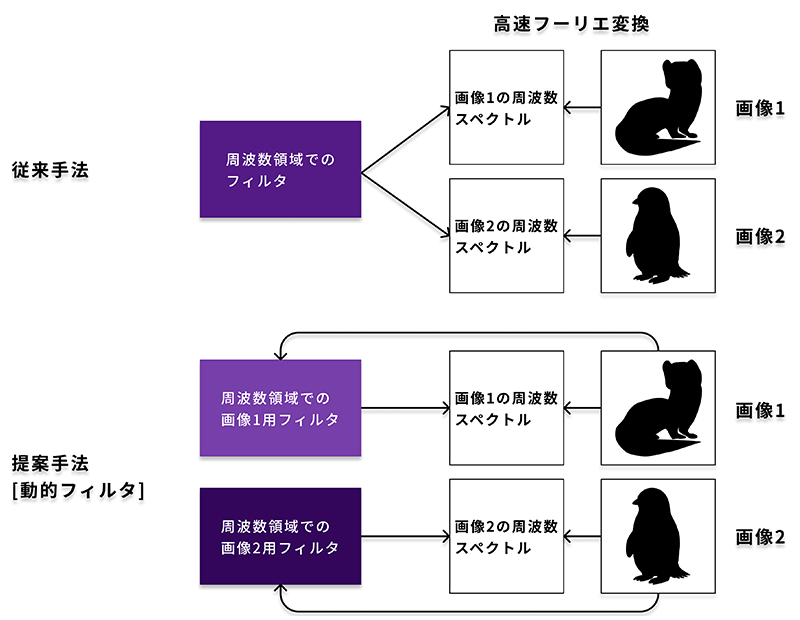
Dynamic filter diagram
Future prospects
Keywords
- AAAI (AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence): A top international conference on artificial intelligence
- Computer vision: A field of computer image recognition and processing
- Attention mechanism: A mechanism with a deep learning model that self-determines and focuses on important information to understand the data it contains. It mimics the cognitive system by which an organism recognizes a target by focusing only on important information.
- Convolution: A method of extracting information from images and the like by integrating local information. It is a kind of filtering.
- Convolutional neural network: A neural network that uses the convolution operation and is dedicated to images
- Fourier transform: A mathematical technique for decomposing signals such as voices and images into different frequency components
- Fast Fourier transform: An algorithm that efficiently computes the Fourier transform
Article information
- Title: FFT-based Dynamic Token Mixer for Vision
- Authors: Yuki Tatsunami, Masato Taki
- Link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2303.03932