Diet, health keys to happy living in the 100-year life era
Professor Katsumi Sugiura(Department of Sport and Wellness)
May 07, 2019
OVERVIEW
With the arrival of a super-longevity era, living for 100 years will become a reality for more and more Japanese. What should people be aware of, and what attitude should they have, to ensure they live a healthy and full life in this time of unprecedented longevity? We asked Professor Katsumi Sugiura for some insights about diet and lifestyle habits that will help people live a long, healthy life.
How is the environment surrounding our health changing?
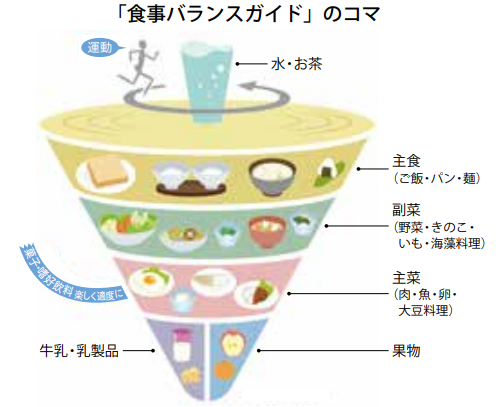
The Japanese Food Guide Spinning Top released by the Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare and the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries indicates what kinds of food and how much one should eat daily. This spinning-top-shaped chart featuring illustrations of food is divided into five meal groups, each indicating a type of food and recommended number of daily servings.
During Japan’s impoverished postwar period, the importance of eating proper meals became widely recognized. As cars become more affordable and used increasingly in daily life, many people stopped getting enough physical exercise. This prompted sports promotion movements and culminated in enactment of the Basic Act on Sport and establishment of the Japan Sports Agency. In recent years, people have begun to realize again how important it is to sleep and rest well to alleviate or prevent problems linked to overwork and depression.
Health indexes have transformed to better reflect these social changes. Today, it is essential to have a well-balanced diet and ensure you get enough exercise and sleep/rest. Information about various health issues is readily and widely available, so individuals of every age should learn about diet and health and review their lifestyle habits.
The link below, “Daily diet check sheet for following the ‘Japanese Food Guide Spinning Top,’” provides recommendations on food selection and quantities for a healthy diet and indicates the necessary nutrients each person should consume daily in accordance with their gender, age and physical activity. You can easily check if you have a balanced diet with this chart.
【Web】English version, “Japanese Food Guide Spinning Top”
Source: Promotion of Shokuiku (food and nutrition education), Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries
How should we approach food, which is vital for good health?
We live in an age of plentiful food, which has made obesity and high blood pressure due to overeating more common. Consequently, society has reached a stage where being especially aware of food’s third function is crucial. To help people maintain a well-balanced diet, various supplements have been put on the market. In Japan, there is no government-set definition for supplements, but they are collectively referred to as foods that allow people to take in certain nutrients. Supplements include green vegetable juice, health foods and energy drinks.
I researched and developed sport supplements at a food maker for many years. Using supplements well can improve body functions and enhance performance. Of course, you should try to have a balanced diet, but taking supplements is a good idea if you need additional nutrients. I recommend checking your daily nutrient intake by looking at the Japanese Food Guide Spinning Top on the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries website.
Make sure you understand the merits and limitations of supplements. Do not jump into trendy products. I recommend taking products made by domestic companies, rather than imports, whose safety sometimes cannot be fully confirmed.
What diet and health challenges lie ahead?
University students decide for themselves how they spend their time, unlike children up to high school age. The same goes for what and when they eat. University years are a transition period during which students begin to manage their own lives, so this is a good opportunity to teach them again about food and how important food is. Acquiring good eating habits before entering society as adults should enable them to reduce the risk of developing lifestyle-related diseases in the future.
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been increasingly put to practical use in various fields. AI will be used also in health fields that closely affect our lifestyle. There are already apps that can calculate a meal’s calories by checking an uploaded photo or visualize the user’s amount of physical activity and sleeping hours. I am certain one can live a healthy, full life by using such technologies and being mindful about lifestyle management.
Professor Sugiura’s three key points
2.Use supplements adequately to boost intake of nutrients in a daily diet.
3.Food and nutrition education is especially necessary for university students, who usually undergo major lifestyle changes.
RECENT TOPICS
Oct 17, 2025
MSDA Rikuzentakata Field Trip 2025
Master of Social Development and Administration (MSDA) Course
PROFILE
Professor Katsumi Sugiura(Department of Sport and Wellness)
A specialist in sports nutritional science, he has given lectures in fields including food and nutrition education, improving elderly people’s physical strength and the appropriate use of supplements. He was nutrition adviser for Japan’s national team during the 2002 Soccer World Cup in Japan and South Korea. His major works include “Katsu karada wo tsukuru! Protein Book” (the English title is “ Protein book –get an athlete’s body & high performance”) published by Ski Journal in 2005, and “Senshu wo shokuji de tsuyoku suru hon” (the English title is “ A winning nutritional guide for athletes”), published by Chukei no Bunko in 2007.